ByJouni Koistinen Jul 24, 2023 1:33:09 PM
The customer's buying journey is a crucial part of a company's business, but how much does it actually cost? The cost of the buying journey varies depending on the chosen digital strategy. The foundation is built when the cost of traffic, the cost of leads, and the value provided to the dream customers are identified. The company needs to identify where it stands in digital marketing and where it wants to go. I have created a description of four different stages of developing a digital strategy.
A company must identify its level in digital marketing and the level it aspires to reach.
A company must be at least at the growth level for the buying journey to work well. It involves building a marketing and sales machine. Behind it, there needs to be a functional marketing technology. The buying journey is a process that builds growth. Would you like to do a baseline analysis together?
It all starts with traffic. Each stage of the Customer journey (conversion) has its own cost, and it must be learned to read in order to get a complete picture of the costs of the Customer journey built through digital marketing and sales. This is where measurement and improvement begin.
Let's start with the marketing budget. Include all other expenses except for the sales team costs. In a well-built system, the costs must be calculated accurately. We are consciously simplifying this model now.
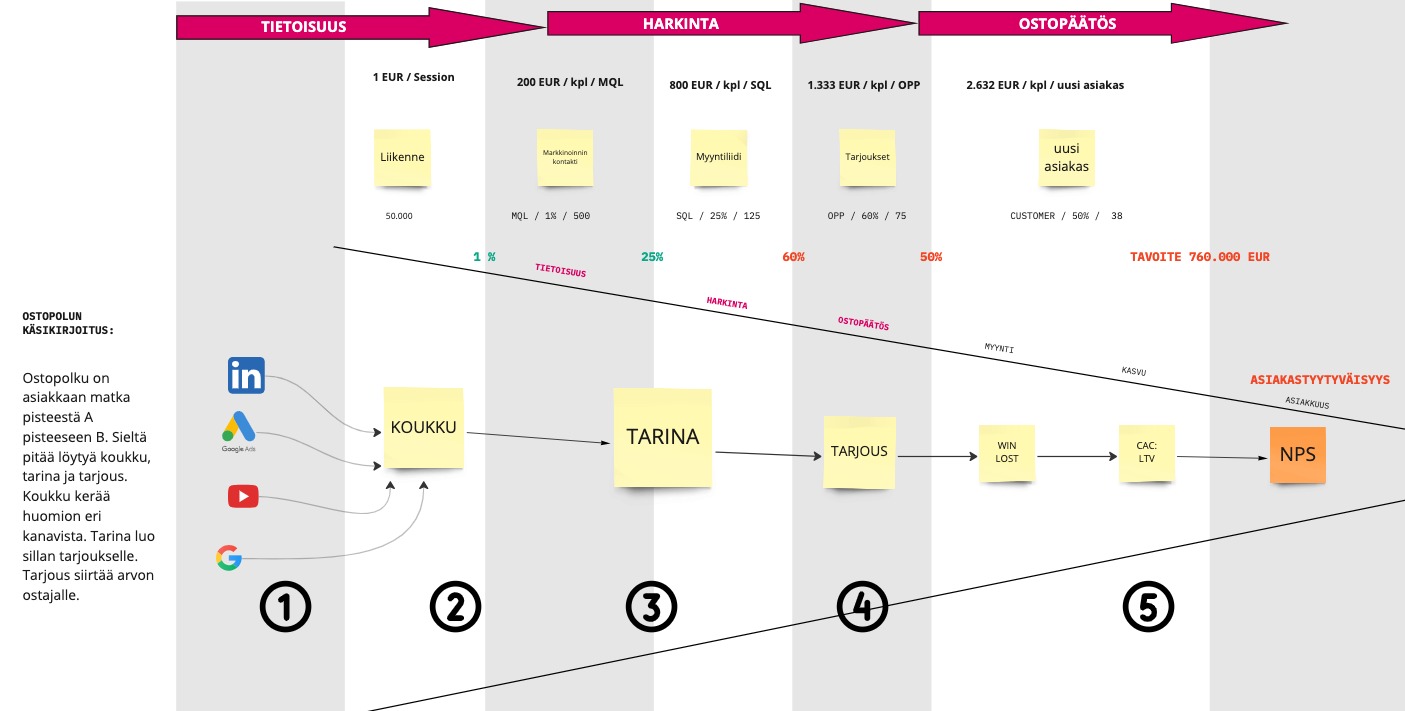
1. Carefully choose the channels where content work is invested. You don't have to be present in every channel. It's a fact that dream customers are not only in one place, but you don't need to be everywhere to get attention. Don't focus on impressions, but evaluate the number and cost of clicks. Budget the creation, maintenance, and purchase of channels separately.
2. Each channel, including paid ones, should have a clear content plan. For each click, there must be a reason to enter the buying journey. The danger is that the message of the buying journey doesn't come across or inspire in the channels. The hook needs to be carefully thought out. The reason to click is personal, meaning what problem the visitor will find a solution to if they proceed to the buying journey.
3. The buying journey conveys the company's story and vision of the dream customer's needs and problems. A good buying journey story includes a promise, proof, problem, solution, context, and call to action. The buying journey is rarely just one landing page. From the problem-solving page, one can move to the sales page and from there to booking, requesting a quote, or making a purchase. This implementation requires good marketing technology and analytics.
4. Without a perfect offer, the buying journey remains incomplete. The meeting between sales and prospect is the first point in the company's buying journey where costs can turn into profits. Therefore, the dream customer must receive a perfect offer that solves their problem. Through the offer, the company's service promise is transferred to the buyer in full value. The buying journey is about guiding the customer to make the purchase decision.
5. The customer's buying journey pays off when the company grows profitably. Multipliers matter. In this example, the return on investment ratio is 7.6 (CAC: LTV) based on a narrow one-year perspective. If it's a service that the customer orders, for example, for the next three years, the ratios would sing hallelujah. The most important thing is to know the cost of each stage and guide marketing and sales towards profitable choices.
In the midst of growth, the most important strategy is to control the customer acquisition cost (CAC) and build tactical models to lower the acquisition cost. All the risks of the buying journey (1-5) must be manageable with data to make the right decisions.
How is it done? Do you want to discuss the model with a digital strategist?